

Copyright © 1995-2004 OnLineTexts.com, Inc. - All Rights Reserved
 If the price of one of the goods changes the slope of the budget constraint must change. On the graph to the right we show the case in which the price of an evening at the club falls from $60 to $40. If our consumer spends all her $1,200 entertainment budget on Club visits she can now afford 30.
If the price of one of the goods changes the slope of the budget constraint must change. On the graph to the right we show the case in which the price of an evening at the club falls from $60 to $40. If our consumer spends all her $1,200 entertainment budget on Club visits she can now afford 30.
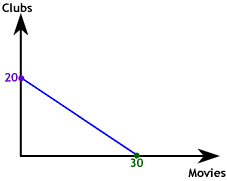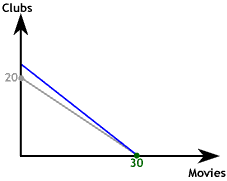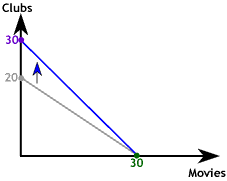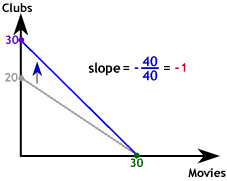
The slope of the budget constraint is the negative of the ratio of the prices of the two goods. Both goods now cost the same so the slope is -1. The opportunity cost of one activity in terms of the other is just -1 since they cost the consumer the same amount.


Copyright © 1995-2004 OnLineTexts.com, Inc. - All Rights Reserved