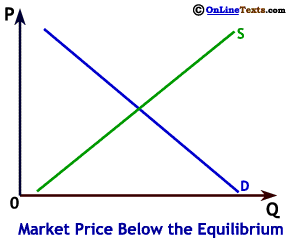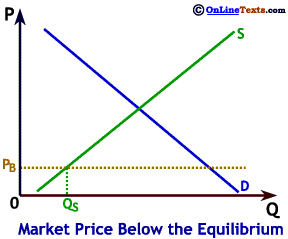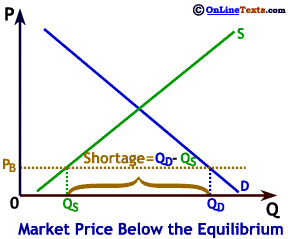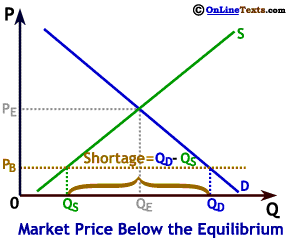
To the right we show a market where the market price, PB, is below the equilibrium price. At price PB the desired quantity supplied is only QS but the desired quantity demanded is QD, leading to a large shortage equal to QD - QS. Many buyers aren't able to purchase the good because the quantity that was produced is less than the quantity demanded. In the case of the market shown to the right, most consumers who would like to buy at price PB will be unable to find any of the product for sale.
Markets where the price is below the equilibrium price are very common. Sold out concerts, sporting events, plays and movies are all examples of markets where the price is below the equilibrium. Many people are opposed to, and some localities have laws against ticket scalping, but scalpers15 would have a hard time surviving if tickets were sold at the equilibrium16 price.


A ticket "scalper" is someone who buys tickets to an event she believes will be sold out so the tickets can be resold later at a higher price.
16There are several reasons why prices may stay below the equilibrium for such events. Among these is that promoters wish to avoid being accused of charging unfair prices. Luxury boxes and other premier seating options enable promoters to charge prices closer to the equilibrium to some attendees, while still maintaining some lower priced seating.