

Copyright © 1995-2004 OnLineTexts.com, Inc. - All Rights Reserved
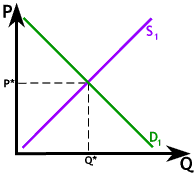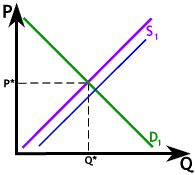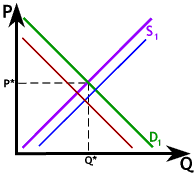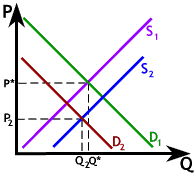 Our final case is a decrease in demand with an increase in supply. In this case, both shifts work to reduce the equilibrium price; however, they work in opposite directions with respect to the equilibrium quantity. Therefore, we must conclude that the change in the equilibrium quantity is indeterminate.
Our final case is a decrease in demand with an increase in supply. In this case, both shifts work to reduce the equilibrium price; however, they work in opposite directions with respect to the equilibrium quantity. Therefore, we must conclude that the change in the equilibrium quantity is indeterminate.
In the graph to the right, the equilibrium quantity decreases slightly. However, it could just as well have increased had supply shifted out a bit more (or had demand shifted back a bit less). Therefore, the change in equilibrium quantity could increase, decrease or remain the same depending on the amount of each shift. Hence, the indeterminacy of the equilibrium quantity.


Copyright © 1995-2004 OnLineTexts.com, Inc. - All Rights Reserved