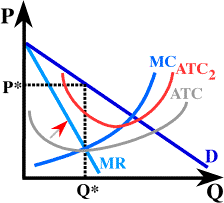
 Annual earthquake insurance premiums only make sense as a fixed
cost since the insurance premiums don't change with each meal
sold or not sold. As we learned, and as shown above, an increase
in fixed costs doesn't affect profit maximizing price and output
for the firm since neither marginal revenue nor marginal cost
change. So, there should be no change in price or in number of
meals sold.
Annual earthquake insurance premiums only make sense as a fixed
cost since the insurance premiums don't change with each meal
sold or not sold. As we learned, and as shown above, an increase
in fixed costs doesn't affect profit maximizing price and output
for the firm since neither marginal revenue nor marginal cost
change. So, there should be no change in price or in number of
meals sold.
6. Suppose a small town in Northern California has only one restaurant.
Suppose the annual earthquake insurance premiums for that restaurant
increase. Which of the following would we expect in the short-run:
- An increase in prices and no change in the number of meals sold.
This would require a simultaneous increase in demand and an increase
in variable costs.
- An increase in prices and a decrease in the number of meals sold.
This would be true only if variable costs rose.
- No change in prices and no change in the number of meals sold.
- A decrease in prices and no change in the number of meals sold.
This would require a simultaneous decrease in demand and an decrease
in variable costs.
- An decrease in prices and an increase in the number of meals sold.
This would be true only if variable costs fell.
Next Question
Copyright © 1995-2004 OnLineTexts.com, Inc. - All Rights Reserved

